Introduction
Within the circles of endurance sports, athletes and coaches are perpetually in search of dietary interventions that can not only enhance performance but also expedite recovery. The study titled “Coffee Increases Post-Exercise Muscle Glycogen Recovery in Endurance Athletes: A Randomised Clinical Trial” provides a groundbreaking insight into how decaffeinated coffee may play an influential role in post-exercise muscle glycogen resynthesis, a crucial aspect of recovery for endurance athletes.
The Role of Muscle Glycogen in Endurance Sports
Understanding Glycogen’s Function
Glycogen serves as the primary storage form of carbohydrates in the body and is a key fuel source during prolonged, intense exercise. The ability to rapidly replenish glycogen stores post-exercise is a cornerstone of effective recovery and subsequent performance.
The Study’s Findings on Glycogen Resynthesis
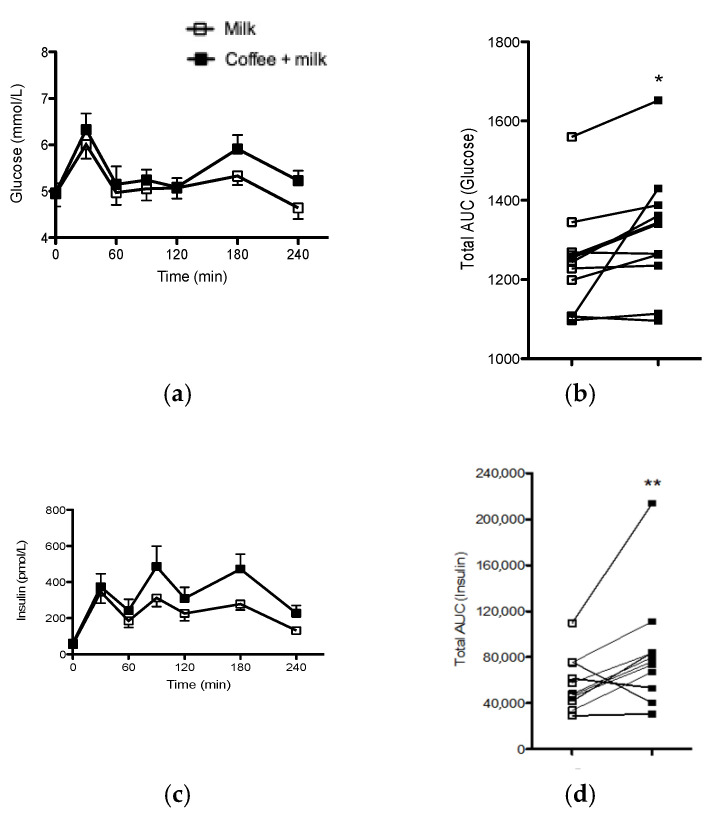
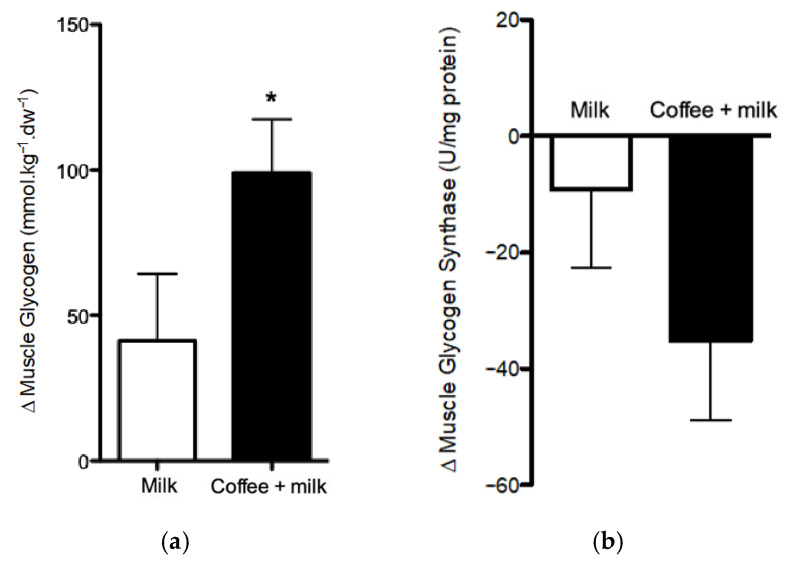
The study presents compelling evidence suggesting that the intake of decaf coffee, when paired with milk, significantly enhances the resynthesis of muscle glycogen after exhaustive exercise compared to the ingestion of milk alone. This is visually represented in the study’s Figure 1, which illustrates the glucose and insulin responses to the two different beverages.
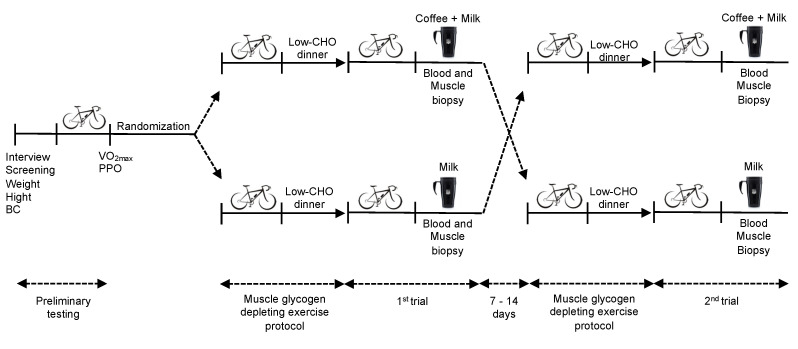
Methodology and Participant Selection
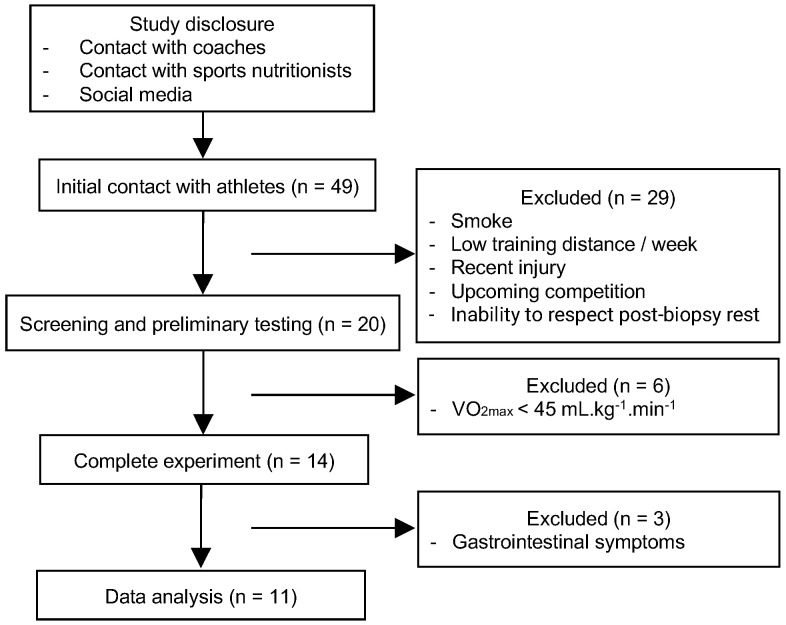
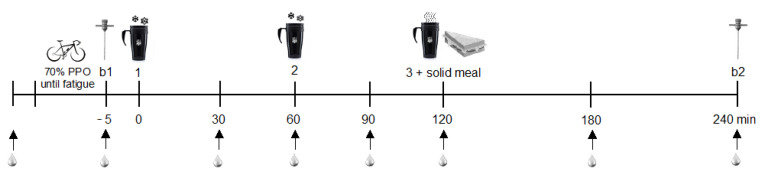
The researchers designed a meticulous and robust methodology to investigate the effects of decaf coffee on muscle glycogen recovery. Through a double-blind crossover randomized clinical trial, they provided substantial data that could alter the nutritional practices of endurance athletes worldwide. The detailed selection and exclusion criteria, depicted in Figure 3 of the study, underscore the validity and reliability of the findings.
The Biochemical Impact of Decaf Coffee
Decaf Coffee and Insulin Sensitivity
It was found that decaf coffee significantly affected metabolic responses post-exercise. Notably, it increased the total area under the curve (AUC) for insulin, as illustrated in Figures 2 and 3 of the study (see above). This enhanced insulin response is conducive to more efficient glycogen storage, facilitating a faster recovery process.
Potential Mechanisms at Play
While the study does not definitively pinpoint the mechanisms through which decaf coffee augments glycogen resynthesis, it hypothesizes that coffee’s bioactive compounds, such as caffeine, cafestol, and caffeic acid, may improve glucose metabolism and promote muscle glycogen recovery when consumed post-exercise. This is an area ripe for further research, as understanding the underlying mechanisms can lead to more targeted nutritional strategies for athletes.
Practical Applications for Endurance Training
Integrating Decaf Coffee into Recovery Protocols
Given the study’s findings, athletes and coaches might consider incorporating decaf coffee into post-exercise nutrition. The evidence suggests that doing so could significantly impact recovery times and preparedness for subsequent training sessions or competitive events.
Considerations for Daily Training
The implications of this study are particularly relevant for athletes undergoing daily training sessions or back-to-back competitive events where the window for recovery is limited. The potential for decaf coffee to expedite glycogen resynthesis could be a game-changer in such scenarios.
Future Directions: Impact of Decaf Coffee
The study concludes that the addition of decaf coffee to a carbohydrate-rich post-exercise beverage is an effective strategy to enhance muscle glycogen recovery, especially for athletes with short recovery times or during competitions with multiple bouts of exercise. However, the exact components of coffee that drive this effect remain unidentified, warranting further investigation.

