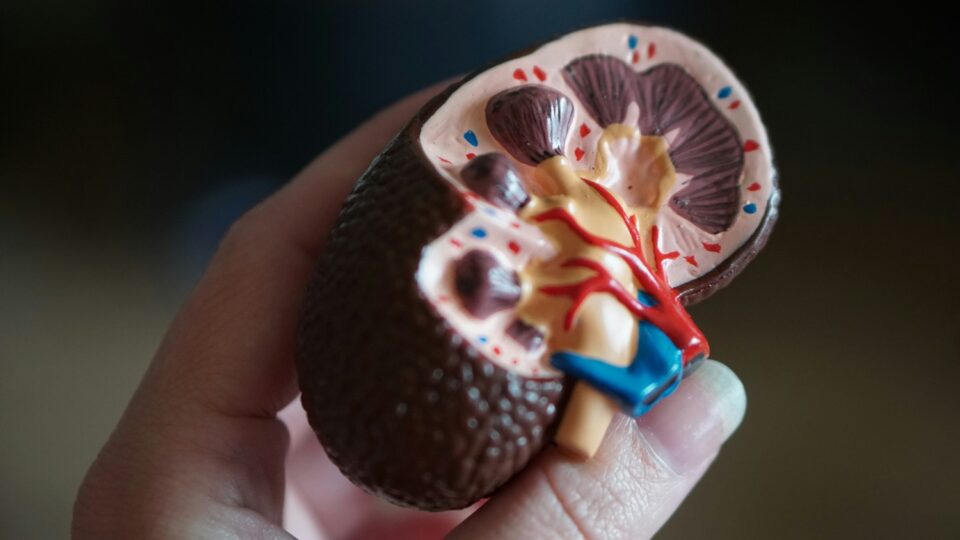
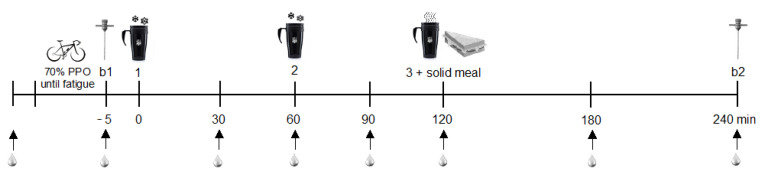
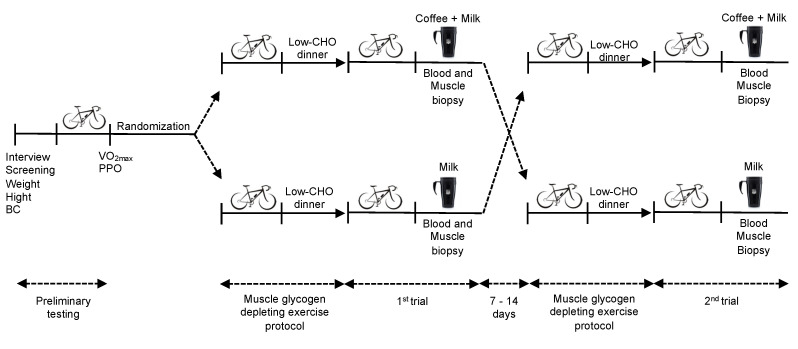
Is Coffee Bad for the Kidneys?
Numerous studies have concluded that coffee is unlikely to harm the kidneys or cause chronic kidney disease (CKD). In fact, research suggests several benefits to consuming a moderate amount of coffee, including improved energy levels and metabolism due to caffeine, as well as the antioxidant properties of polyphenols in coffee. However, moderation is key, especially for individuals with high blood pressure or kidney stones.
Studies on Coffee and Kidney Disease
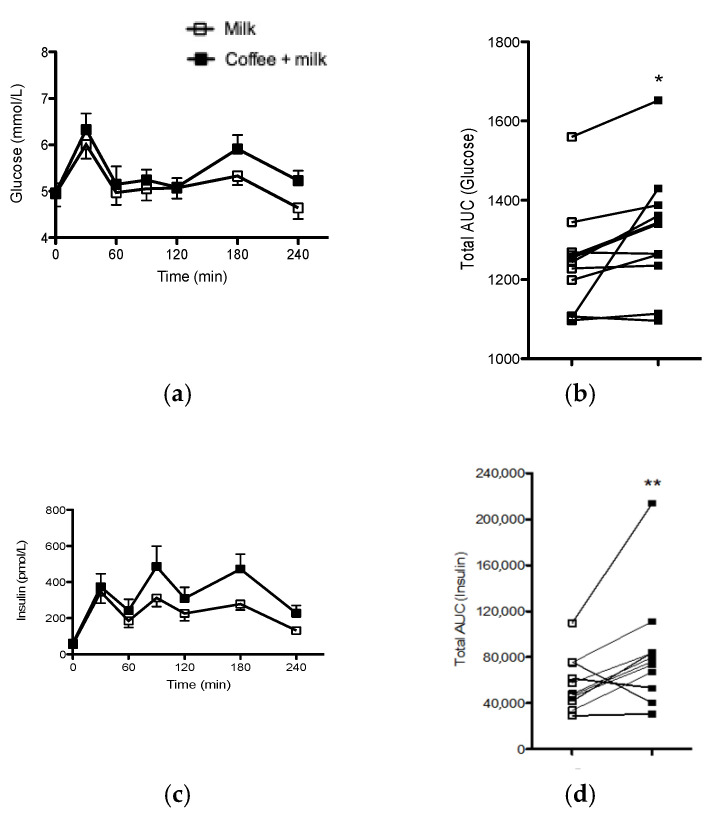
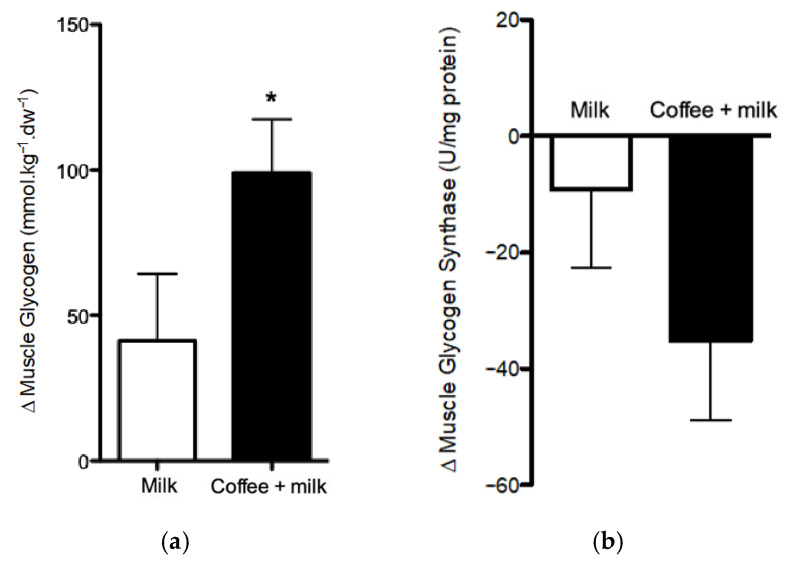
Population-based epidemiological studies have indicated a potential protective effect of coffee consumption on kidney function. For instance, a 2022 study found a lower risk of kidney injury among daily coffee drinkers, with higher consumption associated with greater risk reduction. However, excessive caffeine intake, particularly from caffeinated coffee, may lead to a decline in kidney function, especially in certain populations.
Coffee and Genetic Kidney Disease
Contrary to past concerns, current clinical studies have not found coffee consumption to be a risk factor for the progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD).
Does Coffee Increase the Risk of Kidney Stones?
Regular coffee consumption has been associated with oxalate stone formation, particularly among individuals prone to calcium oxalate stones. Therefore, patients with kidney stones, especially calcium oxalate stones, should consider coffee intake as a potential risk factor.
Does Coffee Increase the Risk of Kidney Cancer?
The relationship between coffee consumption and kidney cancer is mixed. While studies suggest a reduced risk of renal cell carcinoma with caffeinated coffee, decaffeinated coffee may increase the risk of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Further research is needed to understand this association better.
The Relationship Between Coffee, Hypertension, and Kidney Disease
While caffeinated coffee may cause a short-term increase in blood pressure, particularly in older individuals and non-regular coffee drinkers, moderate consumption (up to 3 to 4 cups daily) does not seem to increase the risk of kidney disease in healthy individuals. However, those with high blood pressure should consult with healthcare providers regarding caffeine intake.
Decaf and Hypertension
Even decaffeinated coffee has been associated with increased nervous system activity and blood pressure, suggesting that factors other than caffeine may contribute to this effect.
How to Safely Enjoy Coffee With Kidney Disease: DRINK DECAF COFFEE
For individuals with kidney disease, limiting coffee intake, opting for black coffee to avoid phosphorus and potassium in creamers and milk, counting coffee in fluid allowances, and considering alternative beverages like decaf coffee or teas can help manage kidney health effectively.
Summary
Current research suggests that coffee is generally safe for kidney health, with potential benefits attributed to its caffeine and antioxidant content. However, individuals with specific conditions such as high blood pressure or kidney stones should moderate their coffee intake. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized recommendations is advised.
References
- Antwi SO, Eckel-passow JE, Diehl ND, et al. Coffee consumption and risk of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Causes Control. 2017;28(8):857-866. doi:10.1007/s10552-017-0913-z
- Girardat-rotar L, Puhan MA, Braun J, Serra AL. Long-term effect of coffee consumption on autosomal dominant polycystic kidneys disease progression: results from the Suisse ADPKD, a prospective longitudinal cohort study. J Nephrol. 2018;31(1):87-94. doi:10.1007/s40620-017-0396-8
- Center for Science in the Public Interest. Caffeine chart.
- Sirotkin AV, Kolesárová A. The anti-obesity and health-promoting effects of tea and coffee. Physiol Res. 2021 Apr 30;70(2):161-168. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934674
- Kennedy OJ, Roderick P, Poole R, et al. Coffee and kidney disease. Int J Clin Pract. 2017;71(8):e12980. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12980
- Poole R, Kennedy OJ, Roderick P, et al. Coffee consumption and health: umbrella review of meta-analyses of multiple health outcomes. BMJ. 2017 Nov 22;359:j5024. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j5024
- Harvard Medical School. Coffee and your blood pressure.
- Tommerdahl KL, Hu EA, Selvin E, et al. Coffee consumption may mitigate the risk for acute kidney injury: results from the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Kidney International Reports. 2022;7(7):1665-1672. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.04.091
- Haghighatdoost F, Sadeghian R, Abbasi B. The Associations Between Tea and Coffee Drinking and Risk of Calcium-Oxalate Renal Stones. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2021 Dec;76(4):516-522. doi: 10.1007/s11130-021-00933-4
- Wijarnpreecha K, Thongprayoon C, Thamcharoen N, Panjawatanan P, Cheungpasitporn W. Association of coffee consumption and chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract. 2017;71(1) doi:10.1111/ijcp.12919
- Yamagata K. Do Coffee Polyphenols Have a Preventive Action on Metabolic Syndrome Associated Endothelial Dysfunctions? An Assessment of the Current Evidence. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Feb 4;7(2):26. doi: 10.3390/antiox7020026
- Díaz-López A, Paz-Graniel I, Ruiz V, et al. Consumption of caffeinated beverages and kidney function decline in an elderly Mediterranean population with metabolic syndrome. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):8719. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88028-7